The development of science and technological innovation allow us to create new substances with totally disruptive characteristics. Within this field, the properties of graphene stand out above the rest and place it as one of the materials of the future that offers more opportunities. In this post we explain what it is and what its main applications can be in our day to day.
What is graphene and what is its structure like?
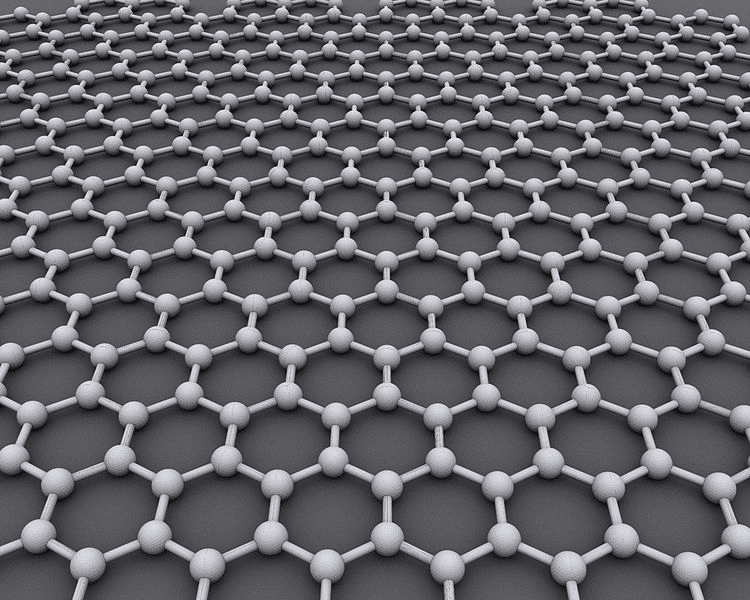
Graphene is a nanomaterial composed of a group of pure carbon atoms arranged in a hexagonal shape and linked by covalent bonds (sp² hybridization). It is characterized by its extreme thinness, since its basic structure constitutes a single layer of one atom thick.
Therefore, the structure of graphene is practically two-dimensional and on a nano-scale, being able to form on a uniform surface compounds between 1 and 10 atoms thick (up to 10 overlapping sheets).
One of the most prominent advantages of graphene is that it is obtained artificially from graphite, which is found abundantly in nature. However, its large-scale production is complex and expensive.
What are the properties of graphene?
The qualities of this allotrope of carbon are revolutionary because it is practically impossible to find them in any other compound in a natural way. We review some of the many properties of graphene:
Resistance
Despite its fine structure, graphene is the strongest material known to date (much stronger than steel).
Hardness
Graphene is also an amazingly hard substance, costing it even more to scratch than diamond.
Conductivity
One of the most practical properties of graphene is its high thermal and electrical conductivity. It also dissipates heat very well and consumes less electricity than silicon.
Flexibility
Graphene is very elastic, malleable and flexible, with the ability to withstand significant forces without deforming.
Lightness
The structure of graphene makes it an ultralight material (five times less heavy than aluminum).
Biocompatibility
When it has been treated and is poorly concentrated, it does not present toxicity to living beings and allows cell growth. In addition, it inhibits the development of bacteria, viruses and fungi.
Reactivity
Graphene has a high reactive potential when it comes into contact with other elements, being able to produce energy. However, it is not affected by ionizing radiation.
Density
It is a very dense material and impervious to liquids and gases, with the sole exception of water. Even so, being water repellent, it evaporates immediately.
Transparency
A single sheet of graphene is almost transparent, although the opacity will increase as layers come together.
Graphene applications
Given its wide range of properties, it is not surprising that graphene applications reach a wide variety of sectors of society. Here are some of them:
Building
The incorporation of graphene can be of great help to build buildings and infrastructures that are more resistant to the passage of time and natural disasters, such as roads, bridges, airports or power lines.
Aeronautical and Automotive Engineering
Given the extraordinary strength, low weight and flexibility of its structure, graphene shows enormous potential for the design of stronger and lighter cars, airplanes, ships and military vehicles.
Electronics
Thanks to its efficient electrical conductivity and its self-cooling capacity, one of the most anticipated applications of graphene is the manufacture of more powerful and durable batteries for electronic devices, such as computers, smartphones and cameras. It will also contribute to the development of flexible touch screens.
Renewable energy
Another of the most promising properties of graphene is its ease of producing energy and transmitting current from one place to another. This is encouraging for the improvement and advancement of clean energies such as solar or wind, thus contributing to caring for the environment.
Medicine
Being a biocompatible product, graphene can be used in the health field to accelerate tissue regeneration, transport drugs, build prostheses and X-ray equipment and even as a biomarker for the detection of cancer cells.
The good news is that many of these utilities are already a reality. Furthermore, given its enormous potential, it is foreseeable that scientific research will contribute in the coming years to an even deeper understanding of the properties of graphene and its practical applications. If you want to stay informed about the latest technological advances in the materials industry, we invite you to continue reading our blog.