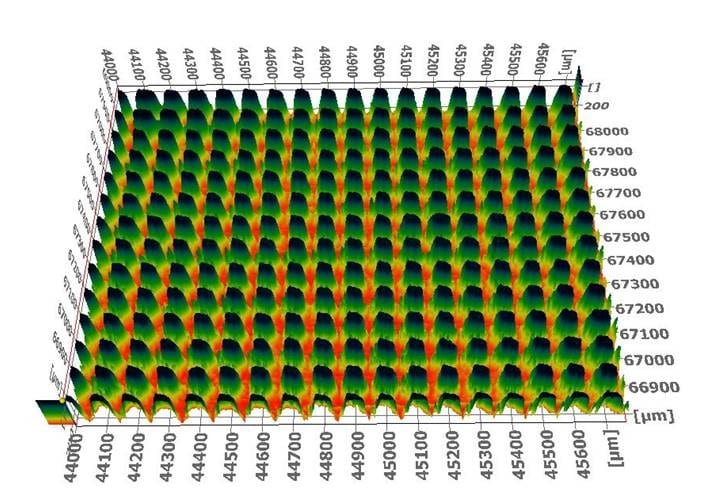
What is the profilometer?
The profilometer is a high-precision piece of equipment used to measure and analyse surface roughness and topography on a variety of materials. Its main function is to provide detailed information on the texture and irregularities of a surface, which is essential in industries where surface finish influences performance, product quality or developing new materials.
Today, roughness control is a key factor in the manufacture of industrial components, as it can affect friction, coating adhesion and the mechanical strength of a material.
In addition to its role in manufacturing, the profilometer is an essential tool in the research and development of advanced materials, such as technological coatings, alloys with optimised properties and functional surfaces. In sectors such as defence and electronics, where surface structure is crucial to device performance, this equipment is used to ensure high-precision finishes.
There are different types of profilometers, contact profilometers, which use a probe to track the surface, and optical or laser profilometers, which use non-contact technologies to obtain three-dimensional measurements with high resolution.
Its ability to evaluate parameters such as roughness, flatness and dimensional profile makes this instrument indispensable in industries such as manufacturing, automotive, aeronautics and materials characterisation.
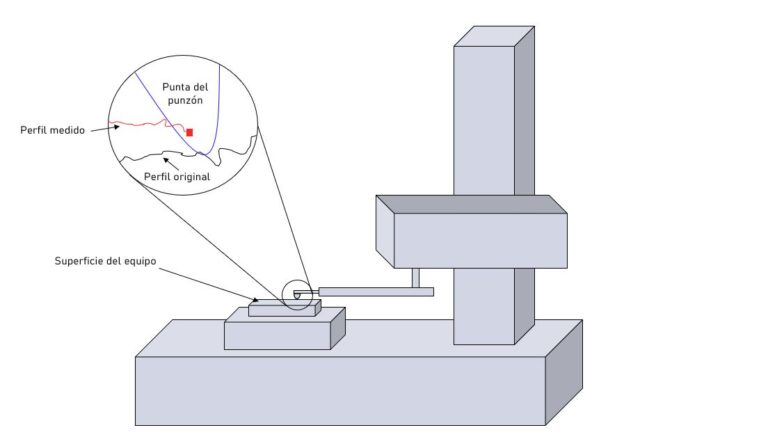
How does the profilometer work?
The operation of the profilometer is based on the capture and analysis of data on the surface of a sample. Depending on the type of profilometer, the measurement can be carried out by mechanical detection or by means of an optical system.
In contact models, a needle or stylus slides over the surface, detecting variations in height which are translated into numerical and graphical values.
In optical profilometers, beams of light are used to scan the surface without touching it, which allows highly accurate roughness maps to be obtained. This technique is particularly useful for the analysis of ultra-thin coatings, where any alteration to the surface can affect its functional properties.
The measurement speed and the type of stylus or laser used can significantly influence the accuracy of the analysis. For example, in industries such as semiconductor manufacturing, extremely precise measurements at the nanometre level are required, making optical profilometers the best choice.
To interpret the results, it is necessary to analyse parameters such as surface roughness (Ra/Rz/Rq), which indicates the variation in surface height, flatness, which measures the uniformity of a sample, and the height of steps or variations in the profile, which allows the precision in the manufacture of parts to be assessed.
Advanced software accompanying modern profilometers allows large volumes of data to be processed and three-dimensional representations of the surface under analysis to be generated . In some recent models, artificial intelligence and machine learning are beginning to be used to identify patterns in surface texture and predict the behaviour of materials under real-use conditions.
The measurement process includes sample preparation, equipment calibration, scan execution and data analysis. These steps ensure reproducible and reliable measurements, essential for quality control and approval of new materials.
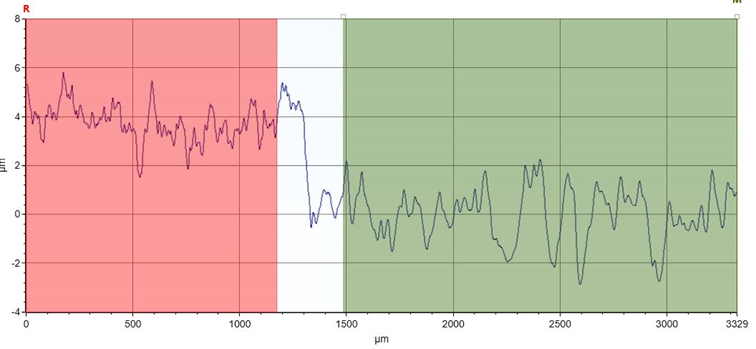
Benefits of the profilometer
One of the main benefits of the profilometer is its ability to perform detailed analysis without destroying the sample, making it an essential tool for surface inspection in industry and research.
Its use ensures that materials and components meet the requirements for finish and functionality, reducing defects in production and optimising the performance of the final products.
Another important aspect is its contribution to reducing waste in manufacturing processes. By detecting irregularities at early stages of production, it prevents the production of defective batches, which in turn reduces costs and improves efficiency.
In addition, its ability to measure in three dimensions provides a more complete view of the surface, facilitating the design and validation of industrial processes.
Profilometer equipment
Bruker’s Dektak Pro, used at INFINITIA , is a high-precision profilometer designed for roughness measurement and detailed surface characterisation. This model has a vertical measurement range of up to 1 mm and a Z-axis resolution in the angstrom range, allowing it to detect minute variations in the topography of the materials under analysis.
Its mechanical probe-based measurement system guarantees consistent results on a wide variety of samples, from ultra-thin coatings to materials with complex geometries. In addition, the DektakXT complies with international standards such as ISO 21920 and ISO 25178, which set the parameters for surface roughness and texture measurement, ensuring that results are comparable and standardised across the industry.
Complementing the profilometer, the scanning electron microscope (SEM) is also used at INFINITIA for advanced surface characterisation, enabling high-resolution imaging and three-dimensional roughness measurements. This combination of techniques provides a more complete and detailed analysis of surface structures, ensuring accurate assessment of materials in sectors such as nanotechnology, microelectronics and functional coatings research.

Equipment applications
The profilometer has multiple applications in different industrial and research sectors. Among its most relevant uses are:
- Surface roughness measurement: This equipment allows you to assess the texture of surfaces with high accuracy, ensuring that they meet the quality standards required in sectors such as automotive, aerospace and electronics manufacturing.
- Profile and dimensional analysis: Used to measure the shape and structure of surfaces, ensuring accuracy in the manufacture of machined parts and the validation of industrial processes.
- Flatness assessment: The ability to measure the uniformity of a surface is essential in the production of optical, electronic and mechanical materials where exact finishes are required.
- Volume and step height measurement: In nanotechnology and microfabrication applications, the profilometer makes it possible to analyse changes in surface height with micrometre resolution, which is essential for the development of high-precision devices.
- Quality control in manufacturing: Used to inspect parts prior to assembly, ensuring that they meet design specifications and preventing failures in final products.
- Coatings and surface treatments industry: Allows the analysis of the adherence and uniformity of paint layers, varnishes and industrial coatings, optimising the protection and aesthetics of materials.
- Materials research and development: In R&D laboratories, the profilometer is an essential tool to study the surface properties of new materials and to improve their performance in different applications.
In conclusion, the profilometer is an essential piece of equipment for surface characterisation in multiple industries, providing accurate data on roughness, flatness and dimensions.
Its ability to analyse materials without damaging them and its versatility in different applications make it a key tool in quality control and advanced materials research.
At INFINITIA, this equipment is used to ensure that the surfaces of materials analysed meet the highest standards of accuracy, forensic engineering analysis to prevent component and material failures, and by professionals looking for reliable, high quality analysis results.
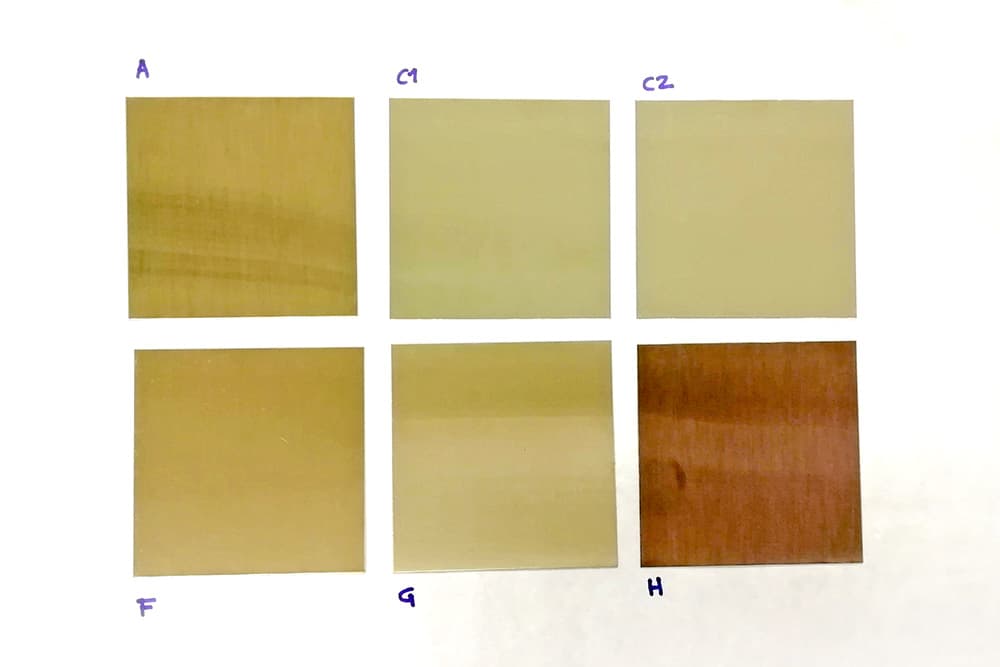
Here are some examples of the use of the profilometer at INFINITIA:
Corrosion resistance comparison for selecting the optimum surface finish