What was the challenge or problem to solve?
A client was interested in conducting an accelerated moisture test to validate the use of new insulating materials proposed by several suppliers. The primary concern was that these materials, due to their composition, could absorb moisture from the environment, potentially increasing their thickness or causing premature decomposition. This phenomenon could compromise the structural integrity and functionality of the material in critical applications.

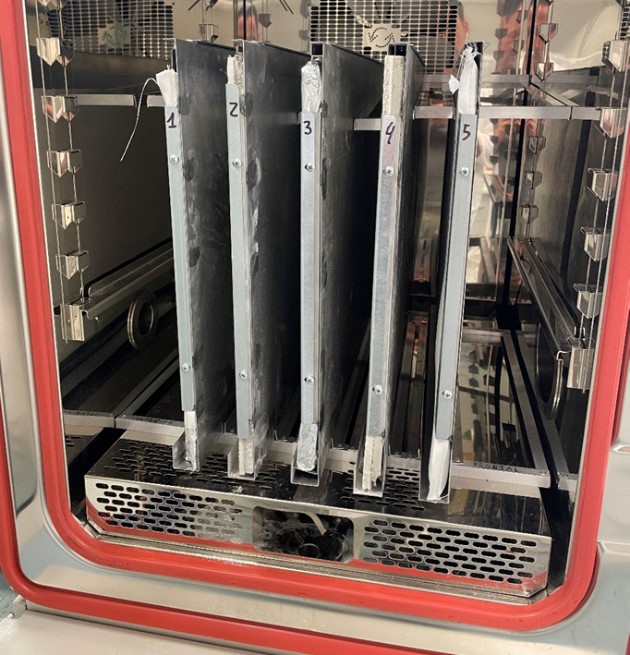
The project’s goal was twofold: first, to adapt and apply relevant industry standards to set up an appropriate testing environment, and second, to evaluate the behaviour of these materials under adverse moisture conditions. The INFINITIA team was tasked with developing a testing methodology that not only complied with applicable industrial standards but also provided reliable data on the viability of the materials in highly humid environments.
The project’s success would be defined by the team’s ability to cross-reference information between different standards and apply various analytical techniques to obtain conclusive results on the adverse effects of moisture on critical insulating materials for the client.
To address this challenge, the INFINITIA Forensic Engineering team broke the project down into several phases. Initially, a review of the relevant standards was conducted to define the critical parameters of the test. This step was crucial to ensure that all experiments were carried out within an appropriate regulatory framework and that the results were relevant to the client’s specific applications.
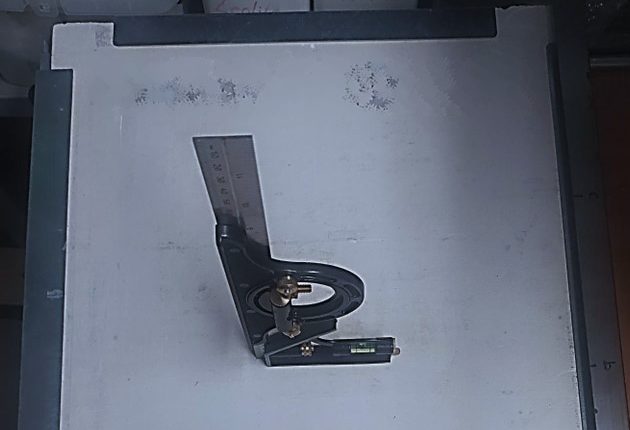
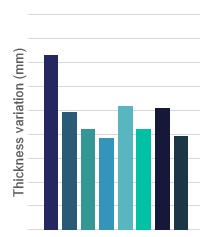
Subsequently, an accelerated aging simulation test was designed and executed. This test involved exposing the materials to controlled humidity and temperature conditions, monitoring critical variables such as the weight and thickness of the materials over time. This phase was vital for obtaining comparative data on the resistance and durability of the materials under study.
Finally, the team compared the different insulating materials to evaluate their viability. Through rigorous testing, significant differences in the behaviour of each material were identified, allowing for the selection of the most suitable material for the client’s specific needs. This process not only confirmed the ability of some materials to better withstand moisture conditions but also highlighted those that were prone to rapid degradation.
The benefits obtained from this project included ensuring the quality and reliability of the insulating materials under adverse conditions and strengthening the client’s confidence in the evaluated products.

