What was the challenge or problem to be solved?
The INFINITIA team was commissioned to conduct a comprehensive study to determine which of two materials was most suitable for the manufacture of electrodes under specific operating conditions.
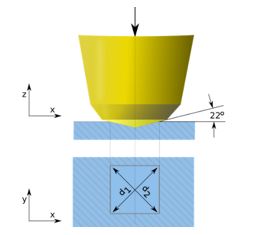
The challenge was to evaluate the durability and wear of the materials under controlled conditions, such as voltage and current, over an extended period of time. This involved detailed and accurate analysis of the samples over time, ensuring that the results were reproducible and representative of actual conditions of use.
The context of this project was the customer’s need to optimise the quality of their products by selecting a material that would guarantee better performance and longer electrode life. This was crucial not only to ensure the functionality of the final product, but also to reduce costs associated with maintenance or premature replacement. The aim was to provide accurate and detailed information on the performance of both materials in order to make an informed decision on which to use in manufacturing.
How was it addressed or what was the solution?
The project began with the design and assembly of an experimental set-up to ensure a controlled and reproducible environment. This step was essential to evaluate the operating conditions accurately and to avoid possible variables that could affect the results. The INFINITIA team worked meticulously to replicate the conditions of use of the electrodes in the laboratory, thus ensuring the reliability of the tests.
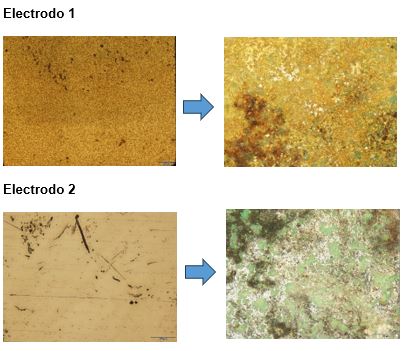
To assess the ageing of the materials, several analytical techniques were used. First, optical microscopy made it possible to observe and document changes in the surface of the electrodes over time. This analysis provided qualitative information on surface wear. Next, scanning electron microscopy (SEM) coupled to an X-ray detector (EDX) allowed further analysis of the wear, detecting changes in the elemental composition of the electrode surfaces.
Finally, the use of potentiometric methods completed the analysis, evaluating the capacitive behaviour of the electrodes after ageing. This comprehensive approach allowed not only to identify the best performing material, but also to understand the reasons behind its better performance. The success of the project was reflected in the ability to provide the customer with conclusive data to select the optimal material, improving the quality and durability of the final product.