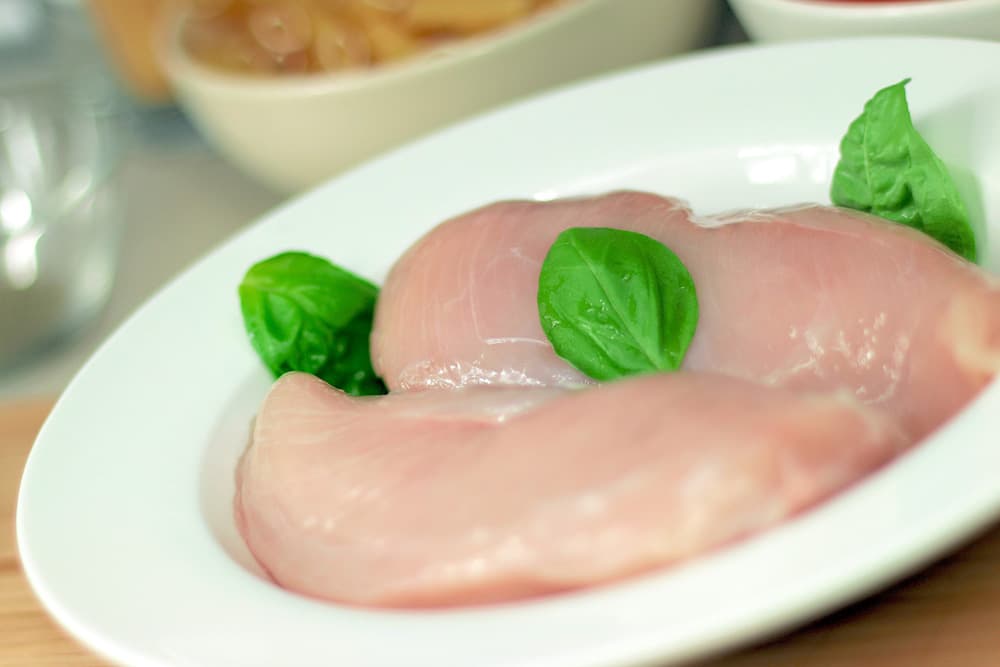
What was the challenge or problem to solve?
The client company informed us of their need to analyse the state of conservation and the appearance of bacteria in foodstuffs, specifically chicken breasts, and to see how to extend their shelf life through different materials or improvements. Microstructured materials have bactericidal properties and offer advantages over other surface disinfection methods. Therefore, the Food Technology team planned a series of test, with the aim of testing the effect of this type of material on the preservation of the breasts.

From this information, it was observed that the samples that had been in contact with the microstructured material showed a lower presence of psychrophilic bacteria. Thus, it was concluded that the microstructured material improves the preservation of chicken breasts and therefore their food safety.
The starting point of this research consisted of a literature search to gather information on the topic in question. A plan of action was then drawn up, whereby microbiological analyses of chicken breasts were carried out on different days. The samples were studied with the help of a Stomacher homogeniser. This equipment in our laboratory allows bacterial determination in foodstuffs with high precision.
With the data obtained, we calculated the CFU/g of mesophilic and psychrophilic bacteria detected in each of the breasts analysed. With this calculation, we were able to determine the number of bacteria in the samples.
Subsequently, the results were interpreted and the final positive assessment of the use of microstructured material in chicken breasts was made.

