What was the challenge or problem to solve?
The main challenge faced by INFINITIA’s Materials team was to develop a set of experiments that would allow for the analysis of surface finishes and obtain valid and applicable conclusions about how different polishing methods affect the wettability of surfaces.

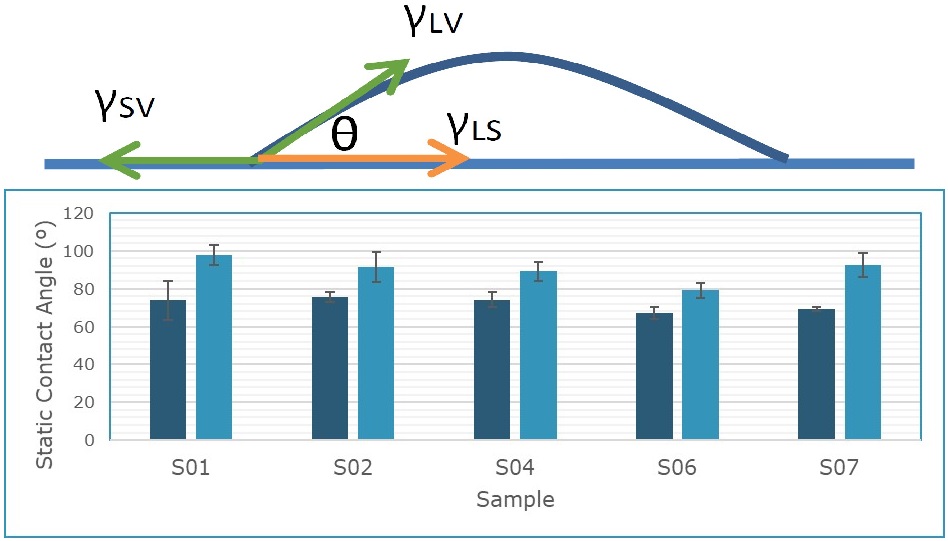
In the field of materials science, the interaction between liquids and surfaces can be fundamental for the development of new industrial applications. One key aspect of this interaction is the contact angle, which measures the tendency of a liquid to spread over a given surface. This angle can be significantly affected by the way the surface has been treated or polished.
The goal was to gain an in-depth understanding of the relationship between different polishing techniques and their effect on the behaviour of various liquids when they come into contact with these treated surfaces. This would not only improve the theoretical understanding of wettability properties but also have practical applications in enhancing industrial processes and products.
The project was structured into three essential phases, starting with the design of the experiments. Initially, an exhaustive literature review was conducted, and discussions were held with our client to select the most relevant polishing parameters and liquids for the tests. This stage was crucial to ensure that the experiments focused on the key variables for the study’s objectives.
Subsequently, the contact angle was measured using an optical tensiometer, a specialized tool that allows for precise evaluation of how liquids interact with treated surfaces. The data collected provided a solid foundation for the final phase of the analysis.
The last step involved detailed statistical treatment of the data, using advanced analytical tools to establish a clear relationship between the applied polishing methods and the wettability of the surfaces. This analysis allowed us to not only validate our initial hypotheses but also to generate a model that can predict the behaviour of liquids based on the polishing conditions of the surfaces.
The benefits obtained from this study are multiple, highlighting the ability to optimize industrial processes and improve the characteristics of final products through a deeper understanding of the wettability properties of treated materials.

